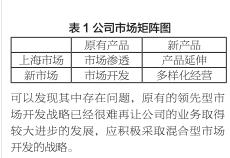
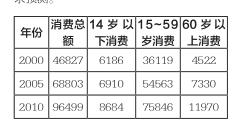
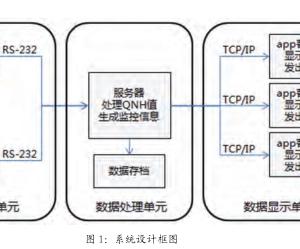
Analysis of Grice’s conversational implicature
收藏
打印
发给朋友
发布者:lunwenchina
热度0票 浏览252次
时间:2019年12月13日 11:01
college of foreign language in Bohai university/Handan【Abstract】 Grice had comprehensive studied on implicaturefrom philosophy view. And proposed the cooperative principleand the way of quality, quantity, relevance, four major principles,it laid a good foundation for the study of the implied. This paperreviews the theory of Grice conversation implicature background,combed the related theory, analyzed the existing problems, andfor the study of linguistics implied, puts forward a new method ofpossible research Angle.
【Key words】 implicature; cooperative principle; Grice1. background
From the thirties of the 20th century, western philosophygradually focused on the methodology. The philosopher stressedthe certainty of knowledge and verifiability. They excludedmetaphysics and try to establish philosophy on the basis ofscience. After that, language philosophy came into being.
Language philosophy mainly concerns alleged, meaning, truthvalue, speech ACTS and so on. Their findings laid a foundationfor the development of modern linguistics, especially thedevelopment of semantics and pragmatics. Many of their view isas a linguistic theories, such as Wittgenstein's theory of meaningand referential, Austin's speech act theory and Grice's cooperativeprinciple, etc. Meaning is derived in terms of its essence, is akind of reasoning phenomenon in verbal communication. Thisphenomenon has noticed by many philosophers. On the basisof criticizing and inheriting predecessors' research, Grice'scooperative principle and its maxims are put forward.
2. relation theory
Implicit phenomenon had been a long time. However,Grice done the most most comprehensive and in-depth research.
For implicature, Grice proposed many relation concepts. Themain concept is: implicature and implicatum; “Natural”
and “unnatural meaning” . Grice created implicature andimplicatum and they are the core concept on implicationresearch. Grice stated:“I wish to introduce, as terms of art , theverb implicate and the related nouns implicature (cf .implying)and implicatum (cf .what is implied ).” (Grice1989 :24)Grice also distinguish say and implicate. Say is relevance toconventional knowledge(vocabulary and grammar) and opposedto implicate. Grice say:“In the sense in which I am using theword say, I intend what someone has said to be closely relatedto the conventional meaning of the words (sentence)hehasuttered.” (Grice 1989:25)
“conventional meaning” is not a linguistic term. No matterwords or sentences with complex semantic structure, what kindof meaning is the conventional has not yet been determined.
There is no clear definition, the implication and meaning of Griceconcept has to continue study. It is obvious that Grice has takenthe meaning of words in relation to the speaker's intention, tohighlight the meaning of subjectivity. “Natural” and“unnaturalmeaning” distinction is also one of the keys to understandthe theory of Grice conversation implicature. All in all, Gricestated conversation as intentional verbal behavior, and proposedimplicature and implicatum, distinguish between natural andunnatural meaning, say and implicate. They are the starting pointof implicature research.
3. Cooperative principle
As a rational communicative behavior, Grice believesthat communication must cooperate, properly, grice thisgeneral principle is called the cooperative principle. Americanphilosopher Paul Grice found that “our talk exchanges donot normally consist of a succession of disconnected remarks,and would not be rational if they did” , and “they arecharacteristically, to some degree at least, cooperative efforts; andeach participant recognizes in them, to some extent, a commonpurpose or set of purposes, or at least a mutually accepteddirection” (Grice:1975:124). In his opinion, in order to makesuccessful and fluent conversations, the participants must firstof all be willing to be cooperative; otherwise, it would not bepossible for them to go on talking. This general principle iscalled the “Cooperative Principle” . People usually abbreviateit as CP, which will be discussed in the following. “We mightthen formulate a rough general principle which participants willbe expected to observe, namely: you’re your conversationalcontribution such as is required, at the stage at which it occursby the accepted purpose or direction of the talk exchange inwhich you are engaged. One might label this the CooperativePrinciple.” (Grice: 1975: 124). Specifically speaking, there arefour maxims under this general principle for us participants tofollow in conversation—the maxim of quantity, the maxim ofquality, the maxim of relation and the maxim of manner.
Quantity
1) Make your contribution as informative as is required (for the current purposes of the exchange).
2) Do not make your contribution more informative than isrequired.
Quality ——Try to make your contribution one that is true.
1) Do not say what you believe to be false.
2) Do not say that for which you lack adequate evidence.
Relation ——Be relevant.
Manner ——Be perspicuous.
1) Avoid obscurity of expression.
2) Avoid ambiguity.
3) Be brief (avoid unnecessary prolixity).
4) Be orderly (Grice, 1975: 125).
Grice's cooperative principle and its criterion is the mainachievements of the studies on the implied. Whether theseprinciples and standards comprehensively and correctly reflectsthe reality in verbal communication? And whether is Universal?
That is to say, in different languages, different social classes,different speech event types, different context, whether allpeople consciously or unconsciously follow these principles andguidelines? In addition, there are besides other principles andstandards. Many scholars focus on these problems.
4. Grice’s Theory of Conversational ImplicatureGrice (1975: 124) pointed out that “I wish to representa subclass of nonconventional implicatures, which I shall callconversational implicatures, as being essentially connectedwith certain general features of discourse” . He proposed thatall speakers, regardless of their cultural background, adhere toa basic principle governing conversation which he termed theCooperative Principle. However, those maxims of CooperativePrinciple are not always observed. Many people do not speakdirectly but express themselves in an implicit way.
Grice made a distinction between quietly violating amaxim and openly flouting a maxim. The former, in Grice’sanalysis, doesn’t lead to implicature. What leads to implicatureis a situation where the speaker flouts a maxim. That is, it isobvious to the hearer at the time of the utterance that the speakerdeliberately and quite openly failed to observe one or moremaxims (Peccei, 2004: 27). Conversational Implicature has beeninvoked for a variety of purposes, from defending controversialsemantic claims in philosophy to explaining lexical gaps inlinguistics. H. P. Grice, who coined the term “ConversationalImplicature,” and classified the phenomenon, developedan influential theory to explain and predict conversationalimplicatures, and describe how they are understood.
Conversational Implicature Theory plays an important role in theresearch of pragmatics.
5. The main question
Grice considered that conversation must obey cooperateprinciple. How to understand the word “cooperation” ? Humanlanguage communication activities is very complex, the policein the criminal trial activities, neighbourhood quarrel, white lies,word games, whether these speech event is “cooperation” ? Inthe adversarial relationship, the communicator will in quality,quantity, relation, manner cooperate? Grice noticed this problemand stated :“… even in the talk-exchange of civilized peoplebrowbeating disputation and conversational sharp practice are fartoo common to be offenses against the fundamental dictates ofconversational practice.” (Grice1989 :369). He also thought:“…whether its tone is agreeable or disagreeable, much of ourtalk-exchange is too haphazard to be directed toward any endcooperative or otherwise . Chitchat goes nowhere , unless makingthe time pass is a journey .” (Grice1989 :369)Obviously, in the implied phenomenon, we must alsoconsider the interrelationships among different language, cultureand communication, and communication activity type may impacton the communication principle.
6. Suggestion and conclusion
Traditional linguistics research methods are describingmethod, inductive method. Language is a hierarchical system.
Communicator use language is the use of the hierarchy system.
So, determine the research level is important. We consider thatlanguage is a very good research point, 1)Sentence is the basic unitsof language communication and it is not isolated, it has relationshipwith the context;2) the statement is the main body, the body is thecommunicator;3) the statement is a speech act. All in all, as the basicunit of language communication, the statement can comprehensivelyreflect the subjectivity, initiative, and comprehensive of nonverbalcommunication. The purpose of the study language is for practicalapplications. Grice's implicit study represents a kind of languagephilosophy research methods. His viewpoint and method makelinguistics (especially pragmatics) benefited a lot. However, if theimplicit study of linguistics became the single philosophical Angle.
That is the sorrow of linguistics. Insist on the distinction betweenlanguage and speech, distinguish between the different languagelevels, implied by describing method, inductive method research isalso a kind of possible choices.
References:
[1]Grice,H.P,Logic and Conversation.In.P.Cole(ed)Readings inLanguage and Mind,Blackwell Publishers,1975.
[2]何兆熊.新编语用学概要[M].上海:上海外语教育出版社,1998.